Tag Archives: sql tutorials online
SQL ORDER BY
SQL ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY Clause is used to sort the data on the basis of columns in ascending or descing order.
SQL ORDER BY Syntax
:
from TableName ORDER By columnName1 , columnName2 ASC | DESC
Note : If We do not use the ASC or DESC keyword the Default order ASC is considered.
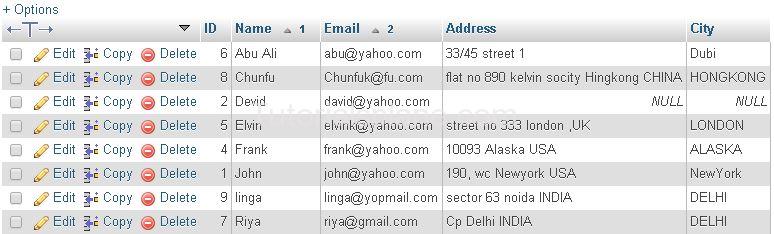
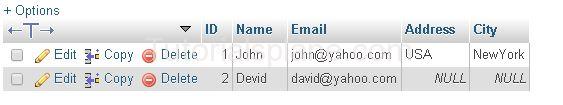
Suppose We Have The Following Data :
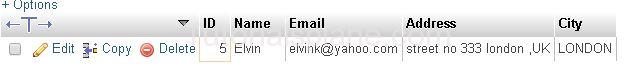
ORDER BY DESC Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in descening order by Id. The Query Produces the result as :
ORDER BY ASC Example :
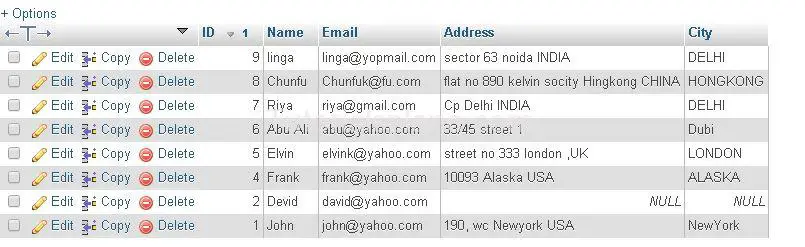
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in ascending order by Id. The Query Produces the result as :
ORDER BY Multiple Columns Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in ascending order by Name & Email. The Query Produces the result as :
SQL – AND & OR
SQL – AND & OR Clauses
SQL – AND & OR Explained
AND Clause :
And Clause displays the results where both the conditions are fullfilled.
OR Clause :
OR Clause displays the results where atleast one conditions is fullfilled.
Suppose we have following data :
AND Clause Example :
Example
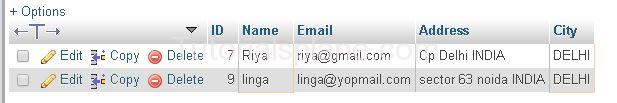
Where [City=”DELHI” and Name=’Riya’] Both Conditions are satisfied.
This Will Produce The Result As :
OR Clause Example :
Example
Where [City=”DELHI” OR Name=’Riya’] Either condition is satisfied.
This Will Produce The Result As :
AND & OR Clause Together Example :
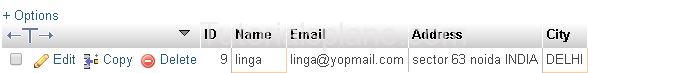
This will select the result where city is (“delhi” or name is “riya” )[produces two rows]
with the condition followed by name “linga” [Selects one from the two rows where name is “linga”]
Example
This Will Produce The Result As :
SQL – WHERE Clause
SQL WHERE Clause
SQL WHERE Clause is used to filter the recoreds on the basis of some condition.
This will fetch the results which will fullfill the condition specified.
SQL WHERE Syntax :
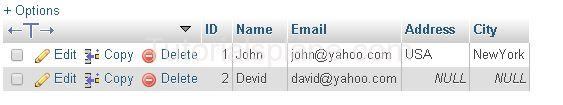
Suppose The “Users” Table has following records :
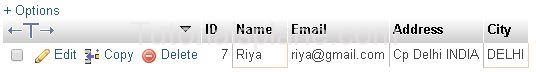
Suppose we have to find those records which have ‘city’ value as “DELHI”
Example 1 – : The Following Example will fetch the results as
Example
The Above Query Will Fetch the results :
Example 2 – : Fetch The Results where user’s ID is ‘5’
Example
The Above Query Will Produce the result as :
SQL – SELECT
SQL – SELECT Statement :
Sql Select Statement is used to fetch records from database table.
SQL – SELECT Syntax 1 (Select All Columns) :
SQL – SELECT Syntax 2 (Select few Columns) :
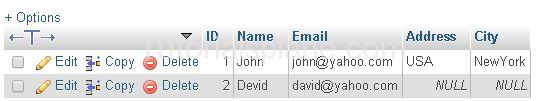
SQL Select All Columns Example :
Example
The above Query will display the results as :
SQL Select Few Columns Example :
Example
The above Query will display the results as :
SQL – INSERT
SQL – INSERT Statement:
SQL INSERT INTO Statement is used to insert a new row(ie. record) in a table.
SQL INSERT INTO Syntax:
Note: The Above Syntax inserts rows in all columns of the table.
If You want to insert values in selected columns the following syntax is used :
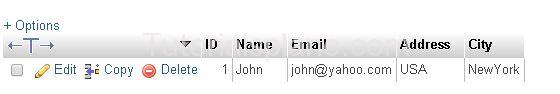
EXAMPLE 1 (Insert in all column) :
Example
1 New row will be inserted.
Now the table has its first record after the selection it will show:
EXAMPLE 2 (Insert in few columns only):
Example
Note: We need to specify the column name in which we want to insert values Like If want to insert values in ID, Name and Email Columns only…
Now the table will look like:
SQL – CREATE TABLE
SQL Create Table Syntax is used to create a table in database .
Tables are collection of rows & columns.
SQL – CREATE TABLE Syntax
(
ColumnName1 datatype,
ColumnName2 datatype,
ColumnName3 datatype,
….
….
….
);
ColumnName1, ColumnName2, ColumnName3, .. are name of columns.
datatype specifies the type of data to be stored in that column example : integer, variable , text or decimal etc..
SQL – CREATE TABLE Example
Example
(
ID int,
Name varchar(100),
Email varchar(100),
Address varchar(100),
City varchar(100),
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
* PRIMARY KEY : Primary creates constraint on the column ID which will contain unique & not null values. We will Explain it in later topics.
Users Table will be created in CustomersDb.
To Verify the table Creation Use The following Command .
Example
Which will Display Created table AS :
SQL – Select Database
To Select database for work use the following syntax :
Syntax for SQL – Select Database
USE Keyword is used to select the database.
Example
You are now switched to database cusetomersdb.
Now you can perform actions like select , create table etc.
SQL – CREATE Database
SQL – CREATE Database Syntax is used to create a database .
Syntax for SQL – Create Database
The Sytax for CREATE Database is
Example
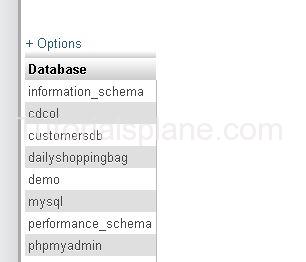
To See the Databases following command is Used.
SHOW DATABASES;
Which will Show the result as :
SQL – Data Types
Most Common used SQL Data types
char(n) : Fixed n numbers of characters accepted(Memory will be Allocated for n character at the time of creation). Max 8,000 characters allowed.
varchar(n) : Variable n numbers of characters accepted(Memory will be Allocated for the character at run time). Max 8,000 characters allowed.
int : Range – whole numbers from 2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
bigint : Range – whole numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807
smallint : Range – whole numbers from -32,768 32,767
tinyint : Range – whole numbers from 0 to 255
decimal : Range Allows decimal numbers from -10^38 +1 to 10^38 -1
numeric : Allows numbers from -10^38 +1 to 10^38 –1.
text : Variable character string. Maximum 2GB of text data can be accepted.
nchar : Fixed size Unicode string. Maximum 4,000 characters allowed.
nvarchar :Variable size Unicode string. Maximum 4,000 characters allowed.
datetime : Range – From 31 Jan, 1753 to Dec 31, 9999
date : Stores date a date From January 1, 0001 to December 31, 9999
time : Store a time example : 1:00 PM